Brightfield & Fluorescence Analysis
In the context of cell segmentation, APS has the capability to identify the following components: positive cells, co-expression, and subcellular signals. Below, we provide a breakdown of the specifics of cell segmentation for the identification of each of these components.
Quantify the positive cell number and the percentage among the whole cell population
Quantify the subclasses of positive cells with different expression level
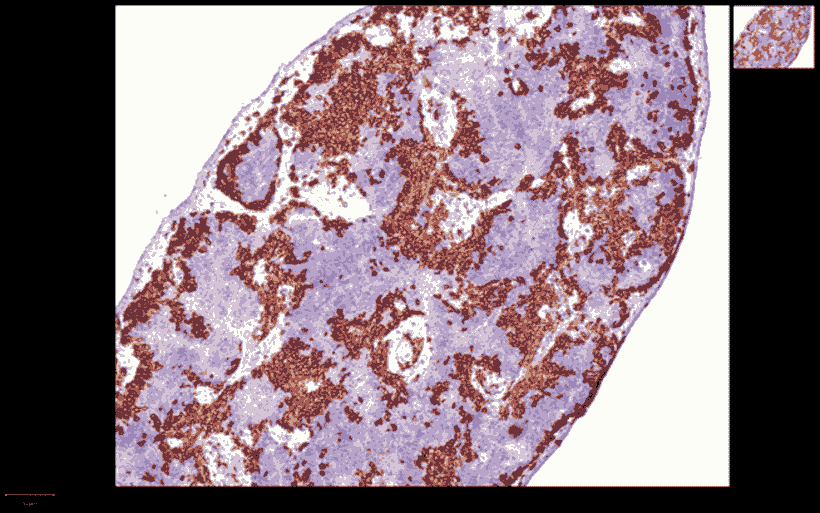
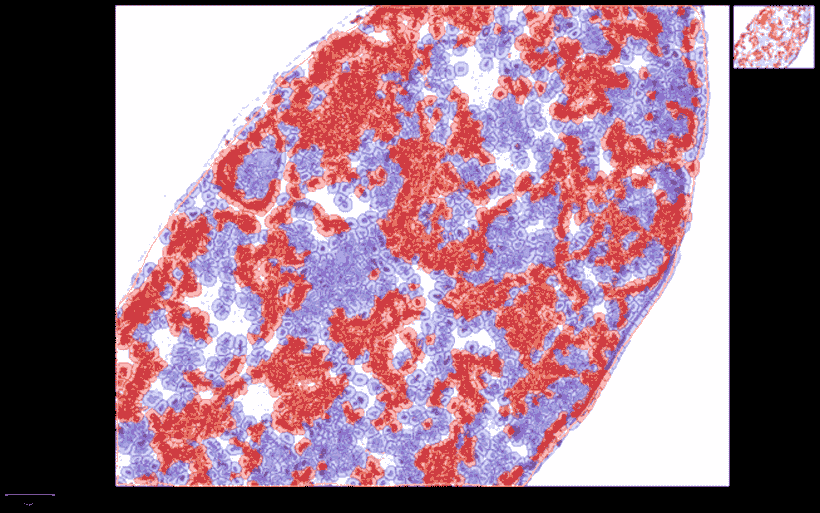
CD-45 IHC Staining in Mouse Spleen
Quantification CD-45 (+) cells in Mouse Spleen
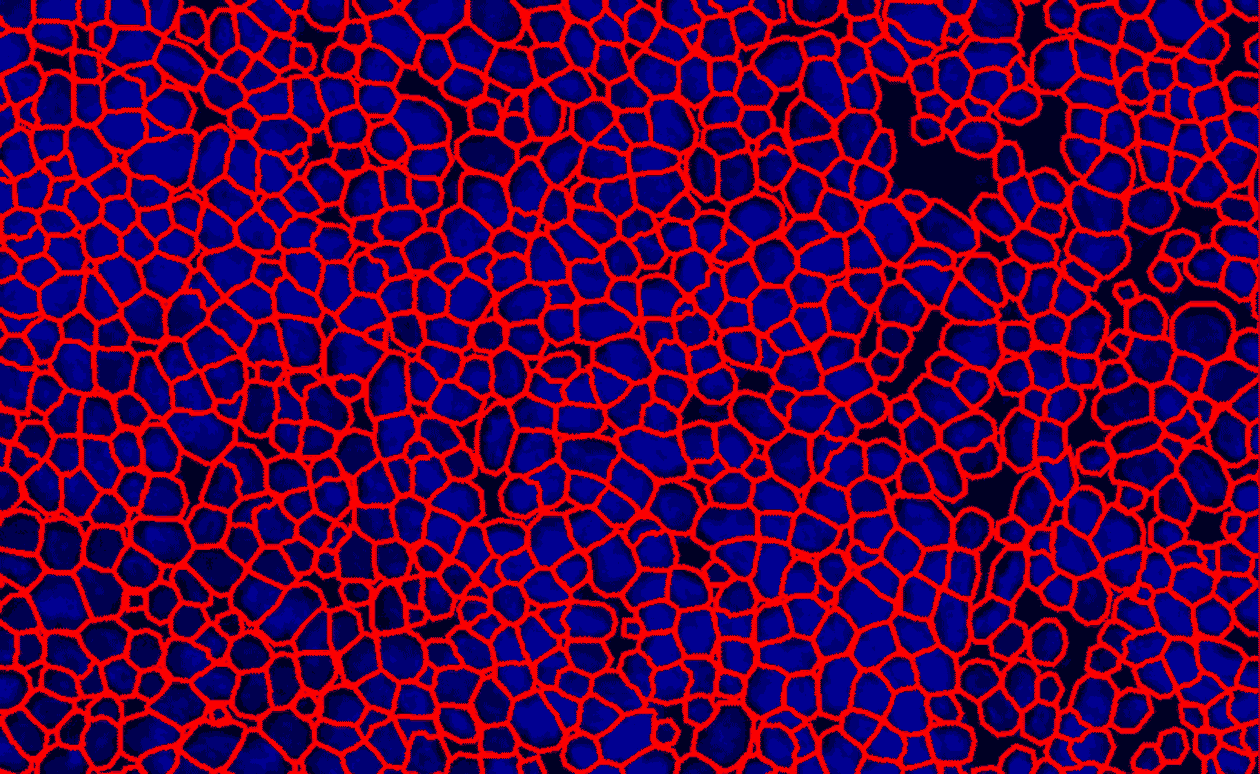
Cell Detection
Quantify the expression of multiple markers in a single cell level.
Quantify the signal intensity in different subcellar compartments, such as nucleus and cytoplasm
to determine the whether the markers are co-expressed and co-localized
common parameters of the exporting data includes percentage of positive cells, percentage of co-expression in total cell population of a classified subgroup of cells in addition to the parameters mentioned
in positive cell detection for each marker
Original Multiplex IHC Image
Nearest CD-68 (+) cells of each CD-20 (+) cell
Nearest PD-L1 (+) cells of each Ki-67 (+) cell